Home » Chili Power : How Capsaicin Eases Pain Naturally

Pain is a common health concern that affects millions of people worldwide. While medications and therapies are often used to manage pain, natural remedies are gaining popularity for their effectiveness and minimal side effects. One such natural remedy is capsaicin, a compound found in chili peppers. Capsaicin has been widely studied for its ability to relieve various types of pain, making it an excellent option for those seeking alternative treatments.
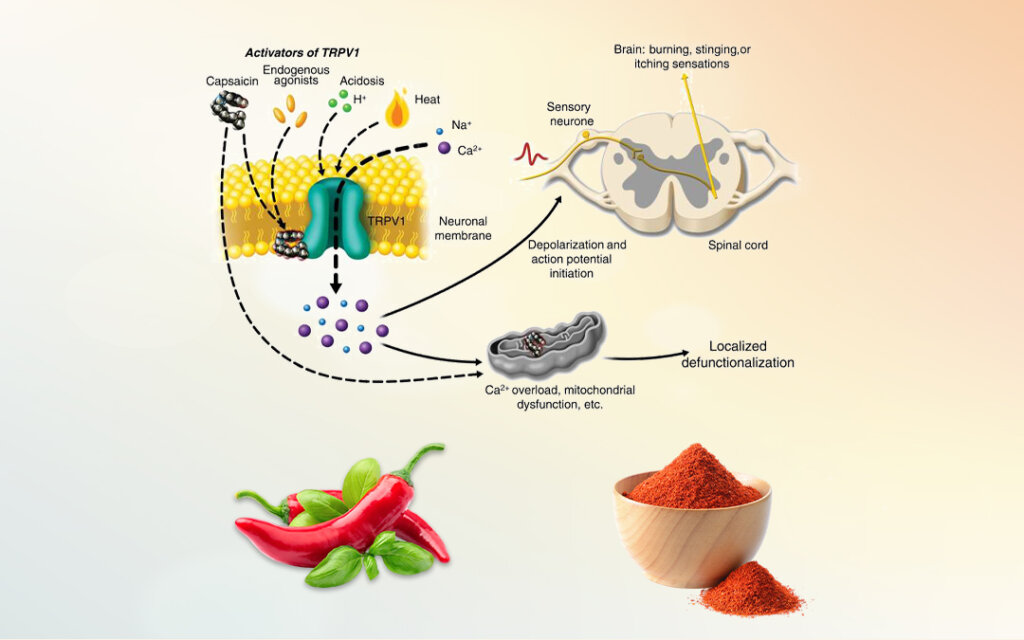
Capsaicin is the active component in chili peppers that gives them their spicy heat. It works by interacting with nerve receptors, particularly the TRPV1 receptor, which is responsible for sensing heat and pain. When applied to the skin or consumed, capsaicin temporarily alters how pain signals are transmitted, leading to pain relief.
Capsaicin is effective in managing pain through the following mechanisms:

Capsaicin reduces pain by depleting substance P, a neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting pain signals to the brain. With prolonged use, this depletion leads to a reduced perception of pain in the affected area.
Repeated application of capsaicin desensitizes nerve endings, making them less sensitive to pain stimuli. This is particularly beneficial for people experiencing chronic pain conditions.
Capsaicin increases blood flow to the area where it is applied, promoting healing and reducing inflammation. Better circulation can help alleviate muscle and joint pain.
Capsaicin has been proven effective in treating various pain-related conditions, including:
* Often used for conditions like diabetic neuropathy, where nerve damage causes burning and tingling sensations.
* Capsaicin patches and creams can provide relief by reducing nerve pain intensity.
* Used in sports creams and balms, capsaicin can help ease muscle tension and post-exercise soreness.
* High-concentration capsaicin patches (8% capsaicin) are used to relieve lingering nerve pain from shingles.
* Some studies suggest that applying capsaicin inside the nostrils may help reduce cluster headaches and migraines.
Capsaicin is available in several forms, depending on the type and severity of pain:
* High-dose capsaicin patches (such as Qutenza containing 8% capsaicin) are available by prescription.
* These patches are applied in a medical setting and can provide pain relief for months.
While capsaicin is generally safe, some precautions should be taken:
* Temporary Burning Sensation: The first few applications may cause a burning feeling, but this usually fades with continued use.
* Avoid Contact with Eyes and Mucous Membranes: Wash hands thoroughly after applying capsaicin creams to prevent accidental irritation.
* Not Suitable for Open Wounds or Sensitive Skin: Avoid applying capsaicin to broken or irritated skin, as it can cause intense burning.
* Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be sensitive to capsaicin; a patch test is recommended before widespread use.
Capsaicin is a powerful natural remedy for pain relief that works by altering pain signal transmission and reducing inflammation. Whether used in topical creams, patches, or dietary sources, it can provide significant benefits for those suffering from chronic pain conditions like arthritis, neuropathy, and muscle pain. However, proper application and precautions are essential to maximize its effectiveness and minimize discomfort. If you are considering capsaicin for pain management, consulting a healthcare professional can help determine the best approach for your specific condition.
Would you try capsaicin for pain relief? Share your experiences and thoughts in the comments below!
Join our mailing list to get updates about our services and procedures or any events and discounts.

WhatsApp us